Briefly explain the traditional and modern methods of capital budgeting?
Briefly explain the traditional and modern methods of capital budgeting?
Similarities
At each point of time a business firm has a number of
proposals regarding various projects in which it can invest funds. But the
funds available with the firm are always limited and it is not possible to
invest funds in all the proposals at a time. Hence, it is very essential to
select from amongst the various competing proposals, those which give the
highest benefits. The crux of the capital budgeting is the allocation of
available resources to various proposals.
There are many methods of evaluating profitability of
capital investment proposals. The
various commonly used methods are as follows:
(A) Traditional methods:
(1) Pay-back Period
Method or Pay out or Pay off Method.
(2) Improvement
of Traditional Approach to pay back Period Method.(post payback method)
(3)
Accounting or Average Rate of Return Method.
(B) Time-adjusted method or discounted methods:
(4) Net Present Value Method.
(5) Internal Rate of
Return Method.
(6) Profitability
Index Method.
(A) TRADITIONAL METHODS:
1.
PAY-BACK PERIOD METHOD
The ‘pay back’ sometimes called as pay out or pay off
period method represents the period in which the total investment in permanent
assets pays back itself. This method is based on the principle that every
capital expenditure pays itself back within a certain period out of the
additional earnings generated from the capital assets.Under this method, various investments are ranked
according to the length of their payback period in such a manner that the
investment within a shorter payback period is preferred to the one which has
longer pay back period. (It is one of the non- discounted cash flow methods of
capital budgeting).
MERITS
The following
are the important merits of the pay-back method:
1. It is easy to calculate and simple to understand.
2. Pay-back method
provides further improvement over the accounting rate return.
3. Pay-back method
reduces the possibility of loss on account of
obsolescence.
DEMERITS
1. It ignores the time value of money.
2. It ignores all cash inflows after the pay-back period.
3. It is one of the misleading evaluations of capital budgeting.
ACCEPT /REJECT CRITERIA
If the actual pay-back period is less than the predetermined
pay-back period, the project would be accepted. If not, it would be rejected.
2. POST PAY-BACK PROFITABILITY METHOD:
One of the serious limitations of Pay-back period
method is that it does not take into account the cash inflows earned after
pay-back period and hence the true profitability of the project cannot be
assessed. Hence, an, improvement
over this method can be made by
taking into account the return receivable beyond the pay-back period.
Post pay-back profitability =Cash inflow (Estimated life –
Pay-back period) Post pay-back
profitability index= Post pay-back profitability/original investment
3. AVERAGE RATE OF RETURN:
This method takes into account the earnings expected
from the investment over their whole life. It is known as accounting rate of
return method for the reason that under this method, the Accounting concept of
profit (net profit after tax and depreciation) is used rather than cash
inflows. According to this method, various projects are ranked in order of the
rate of earnings or rate of return. The project with the higher rate of return
is selected as compared to the one with lower rate of return. This method can also be used to make decision as to accepting or rejecting a proposal. Average
rate of return means the average rate of return or profit taken for considering
(a) Average Rate of Return Method (ARR):
Under this method average profit after tax and
depreciation is calculated and then it is divided by the total capital outlay or
total investment in the project. The project evaluation. This method is one of
the traditional methods for evaluating
The project
proposals
ARR = (Total profits (after dep & taxes))/ (Net Investment in
the project X No. of years of profits) x 100
OR
ARR = (Average
Annual profits)/ (Net investment in the project) x 100
(b) Average Return on Average Investment Method:
This is the most appropriate method of rate of return
on investment Under this method, average profit after depreciation and taxes is
divided by the average amount of investment; thus:
Average Return on Average Investment = (Average Annual Profit after
depreciation and taxes)/ (Average Investment) x 100
Merits
1. It is easy to calculate and simple to understand.
2. It is based on the accounting information rather than cash inflow.
3. It is not based on the time value of money.
4. It considers the total benefits associated with the project.
Demerits
1. It ignores the time value of money.
2. It ignores the reinvestment potential of a project.
3. Different
methods are used for accounting profit. So, it leads to some difficulties in
the calculation of the project.
Accept/Reject criteria
If the actual accounting rate of return is more than the
predetermined required rate of return, the project would be accepted. If not it
would be rejected.
(B) TIME – ADJUSTED OR DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW METHODS: or MODERN METHOD
The traditional methods of capital budgeting i.e.
pay-back method as well as accounting rate of return method, suffer from the
serious limitations that give equal weight to present and future flow of
incomes. These methods do not take into consideration the time value of money,
the fact that a rupee earned today has more value than a rupee earned after
five years.
1. NET PRESENT VALUE
Net present value method is one of the modern methods for evaluating
the project proposals. In this method cash inflows are considered with the time
value of the money. Net present value describes as the summation of the present
value of cash inflow and present value of cash outflow. Net present value is
the difference between the total present values of future cash inflows and the
total present value of future cash outflows.
NPV = Total Present value of cash inflows – Net Investment
If offered an investment that costs $5,000
today and promises to pay you $7,000 two years from today and if your
opportunity cost for projects of similar risk is 10%, would you make this
investment? You Need to compare your $5,000 investment with
the $7,000 cash flow you expect in two years. Because you feel that a discount
rate of 10% reflects the degree of uncertainty associated with the $7,000
expected in two years, today it is worth:
By investing $5,000 today, you are getting in
return a promise of a cash flow in the future that is worth $5,785.12 today.
You increase your wealth by $785.12 when you make this investment.
Merits
1. It recognizes the time value of money.
2. It considers the total benefits arising out of the proposal.
3. It is the best method for the selection of mutually exclusive projects.
4. It helps to achieve the maximization of shareholders’ wealth.
Demerits
1. It is difficult to understand and calculate.
2. It needs the discount factors for calculation of present values.
3. It is not suitable for the projects having different effective lives.
Accept/Reject criteria
If the present value of cash inflows is more than the
present value of cash outflows, it would be accepted. If not, it would be
rejected.
2. PROFITABILITY INDEX METHOD
The profitability index (PI) is the ratio of the present value of
change in operating cash inflows to the present value of investment cash
outflows:
Instead of the difference between the two present values, as in equation PI is the
ratio of the two present values.
Hence, PI is a variation of NPV. By construction, if the NPV is zero, PI is one.
3. INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN METHOD
This method is popularly known as time adjusted rate of return
method/discounted rate of return method also. The internal rate of return is
defined as the interest rate that equates the present value of expected future
receipts to the cost of the investment outlay. This internal rate of return is
found by trial and error. First we compute the present value of the cash-flows
from an investment, using an arbitrarily elected interest rate. Then we compare
the present value so obtained with the investment cost. If the present value is higher than the cost figure, we try a
higher rate of interest and go through the procedure again. Conversely, if the
present value is lower than the cost, lower the interest rate and repeat the process.
The interest rate that brings about this equality is defined as the internal
rate of return. This rate of return is compared to the cost of capital and the
project having higher difference, if they are mutually exclusive, is adopted
and other one is rejected. As the determination of internal rate of return
involves a number of attempts to make the present value of earnings equal to
the investment, this approach is also called the Trial and Error Method.
Internal rate of return is time adjusted technique and covers the disadvantages
of the Traditional techniques. In other words it is a rate at which discount
cash flows to zero. It is expected
by the following ratio
Steps to be followed:
Step1. Find out factor Factor is calculated as follows:
Step 2. Find out positive net present value Step 3. Find out negative net present value
Step 4. Find out formula net present value
Base factor = Positive discount rate DP = Difference in percentage Merits
1. It considers the time value of money.
2. It takes into account the total cash inflow and outflow.
3. It does not use the concept of the required rate of return.
4. It gives the approximate/nearest rate of
return.
Demerits
1. It involves complicated computational method.
2. It produces multiple rates which may be confusing for taking decisions.
3. It is assume that all intermediate
cash flows are reinvested at the internal rate of return.
Accept/Reject criteria
If the present value of the sum total of the compounded reinvested
cash flows is greater than the present value of the outflows, the proposed
project is accepted. If not it would be rejected.
|
|
Key differences between
the most popular methods, the NPV (Net Present
Value) Method and IRR (Internal Rate of
Return) Method, include:
• NPV is calculated in terms of currency while IRR is expressed in terms of the
percentage return a firm expects the capital project to return;
• Academic evidence
suggests that the NPV Method is
preferred over other methods since it calculates additional wealth and the
IRR Method does not;
• The IRR Method
cannot be used to evaluate projects where there are changing cash flows (e.g., an initial outflow followed by in-flows
and a later out-flow, such as may be required in the case of land reclamation
by a mining firm);
• However, the IRR Method does have one significant
advantage -- managers tend to better understand the concept of returns
stated in percentages and find it easy to compare to the required cost of
capital; and, finally,
• While both the
NPV Method and the IRR Method are both DCF models and can even reach similar
conclusions about a single project, the use of the IRR Method can lead to the
belief that a smaller project with a shorter life and earlier cash inflows, is preferable to a larger project that will
generate more cash.
• Applying NPV
using different discount rates will
result in different recommendations. The IRR method always gives the same recommendation.
Recent
variations of these methods include:
• The Adjusted Present Value (APV) Method is a
flexible DCF method that takes into account interest related tax shields; it is
designed for firms with active debt and a consistent market value leverage ratio;
• The Profitability Index (PI) Method, which is
modeled after the NPV Method, is measured as the total present value of future
net cash inflows divided by the initial investment; this method tends to favor
smaller projects and is best used by firms with
limited resources and high costs of capital;
• The Bailout
Payback Method, which is a variation of the Payback Method, includes the salvage value of any equipment
purchased in its calculations;
• The Real Options
Approach allows for flexibility, encourages constant reassessment based on the riskiness
of the project's cash flows and is based on the concept of creating a list of value-maximizing
options to choose projects from; management can, and is encouraged, to react to
changes that might affect the assumptions that were made about each project
being considered prior to its commencement, including postponing the project if
necessary; it is noteworthy that there is not a lot of support for this method
among financial managers at this time.
______________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________'
|
BASIS FOR COMPARISON
|
NPV
|
IRR
|
|
Meaning
|
The total of all the present values of cash flows (both
positive and negative) of a project is known as Net Present Value or NPV.
|
IRR is described as a rate at which the sum of discounted cash
inflows equates discounted cash outflows.
|
|
Expressed in
|
Absolute terms
|
Percentage terms
|
|
What it represents?
|
Surplus from the project
|
Point of no profit no loss (Break even point)
|
|
Decision Making
|
It makes decision making easy.
|
It does not help in decision making
|
|
Rate for reinvestment of intermediate cash flows
|
Cost of capital rate
|
Internal rate of return
|
|
Variation in the cash outflow timing
|
Will not affect NPV
|
Will show negative or multiple IRR
|
Key Differences Between NPV and IRR
The basic differences between NPV and IRR are presented below:
The aggregate of all present value of the cash flows of an asset,
immaterial of positive or negative is known as Net Present Value. Internal Rate
of Return is the discount rate at which NPV = 0.
The calculation of NPV is made in absolute terms as compared to IRR which
is computed in percentage terms.
The purpose of calculation of NPV is to determine the surplus from the
project, whereas IRR represents the state of no profit no loss.
Decision making is easy in NPV but not in the IRR. An example can explain
this, In the case of positive NPV, the project is recommended. However, IRR =
15%, Cost of Capital < 15%, the project can be accepted, but if the Cost of
Capital is equal to 19%, which is higher than 15%, the project will be subject
to rejection.
Intermediate cash flows are reinvested at cut off rate in NPV whereas in
IRR such an investment is made at the rate of IRR.
When the timing of cash flows differs, the IRR will be negative, or it will
show multiple IRR which will cause confusion. This is not in the case of NPV.
When the amount of initial investment is high, the NPV will always show
large cash inflows while IRR will represent the profitability of the project
irrespective of the initial invest. So, the IRR will show better results.
Similarities
- Both uses Discounted Cash Flow
Method.
- Both takes into consideration
the cash flow throughout the life of the project.
- Both recognize time value of
money.


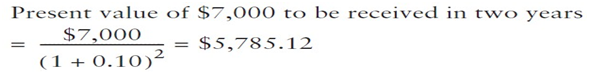








Lifting weights; increasing reps produces more hormones. So bodybuilding itself should do it. The supplements are a rip off!
ReplyDeletejeqing
I have like to read your post. It was good articles for all,Thanks for sharing. https://timelybills.app
ReplyDeleteCool App.
ReplyDeleteHey guys, If you want All in one budget management and bill reminder mobile friendly app for android and ios, do check out @timelybill.app.
Secured app that you Use it for all purpose
Timelybills.app
Low Cost Custom Built Order Management Software | ERP GOLD
ReplyDeleteOrders can be received from businesses, consumers, or a mix of both, depending on the products. with ERP Gold's Low Cost Custom Built Order Management Software you can manage; Product information, Inventory, Vendors, Marketing, Customers/prospects & Orders all at the same time. It is an Easy Order Management Software which helps the user make decisions on order management very easily.
Low Cost Custom Built Order Management Software is specially designed for startups and Small Business so that they won't have to spend a lot of money on softwares and get better results from less investment.
Features of ERP Gold's Order Management Software includes:
It is cloud based with SSL connection
Business Operation Integration
Top Level Security with SSL
Adaptability with fast deployment
For more information, visit our website : https://www.erp.gold/easy-inventory-management-software/
Or Get in touch with us: 1-888-334-4472
Address: Suite 183411, Shelby TWP, MI 48318
Email us: support@erp.gold
Keyword: easy inventory management software
gdn
ReplyDeleteIt further goals to recognize the factors influencing the working capital, its volume, and in the process try to suggest remedial measures which might help in optimizing the use of working capital. It also considers as to how precisely “financing working capital” and further more what should be mix of different components of working capital.Thanks for sharing Valuable Information and it's very helpful. Being Best Top ca Final institute in bangalore One of the Leading Coaching Centres in bangalore for Chartered Accountancy.
ReplyDeleteThese investors focus on certain types of businesses and are often faster than others to grasp developments within a particular industry. These are often groups of professionals from the same industry who keep close tabs on their market and are therefore quicker to recognize risks and opportunities. Major corporations also sometimes acquire equity in companies whose growth they believe it is in their interest to support.Thanks for sharing useful Information for the reasearch and it's very helpful. Being best ca coaching in hyderabad . One of the Leading Coaching Centres in Hyderabad for Chartered Accountancy.
ReplyDeleteThese investors focus on certain types of businesses and are often faster than others to grasp developments within a particular industry. These are often groups of professionals from the same industry who keep close tabs on their market and are therefore quicker to recognize risks and opportunities. Major corporations also sometimes acquire equity in companies whose growth they believe it is in their interest to support.Thanks for sharing useful Information. Being Best ca course fees in coimbatore . One of the Leading Coaching Centres in Coimbatore for Chartered Accountancy.
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing useful Information. These investors focus on certain types of businesses and are often faster than others to grasp developments within a particular industry. These are often groups of professionals from the same industry who keep close tabs on their market and are therefore quicker to recognize risks and opportunities. Major corporations also sometimes acquire equity in companies whose growth they believe it is in their interest to support. Being Best US CMA coaching centre in Coimbatore One of the Leading Coaching Centres in Coimbatore for Chartered Accountancy.
ReplyDelete